How to Increase Virtual Memory RAM on PC & Laptop
What is virtual memory?
Virtual memory is a memory management technique used by operating systems to extend the available RAM (Random Access Memory) beyond physical limitations. Here’s how it works:
- Physical RAM: Your computer has a certain amount of physical RAM (e.g., 8GB, 16GB). This RAM is fast but limited in size.
- Page File (Swap File): When your RAM is fully utilized, the operating system uses a portion of your hard drive (usually a file called the page file or swap file) as additional memory. This virtual memory acts as an extension of your RAM.
- Page Swapping: When an application needs more memory than the available RAM, the OS swaps out less-used data from RAM to the page file. It then loads the required data into RAM. This process is called paging.
- Performance Impact: While virtual memory allows multitasking and prevents system crashes due to low memory, it’s slower than physical RAM. Accessing data from the page file takes more time because hard drives are slower than RAM.
- Customizing Virtual Memory: You can adjust the size of the page file (virtual memory) manually. Larger page files allow more multitasking but may slow down your system if your hard drive is slow. Smaller page files conserve space but may lead to performance issues if RAM is insufficient.
Remember that managing virtual memory involves balancing system performance and available storage space.
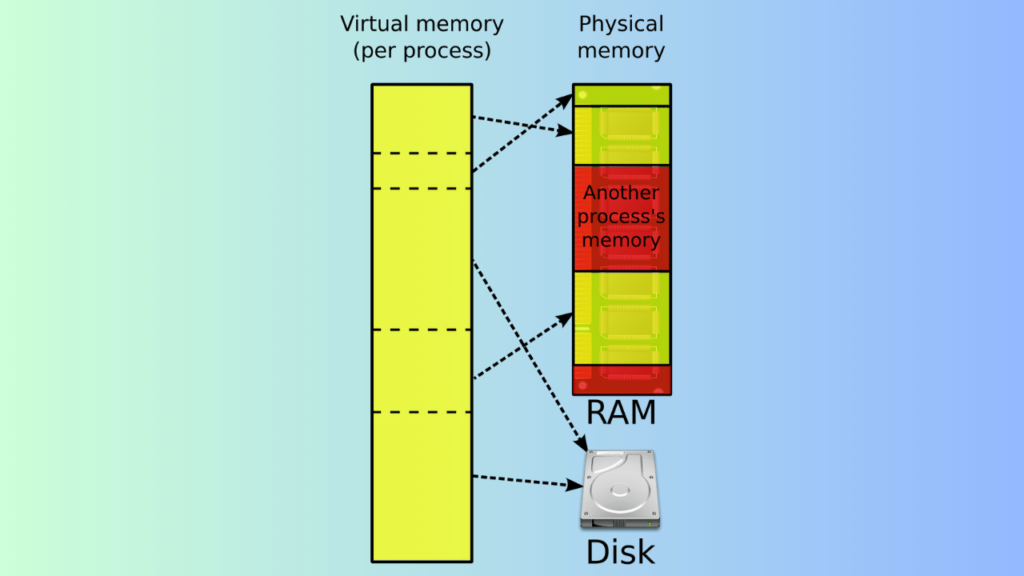
Table of Contents
How to Increase Virtual Memory on Windows 10 / 11
To increase virtual memory on Windows 11, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open the Settings app by pressing Windows + I.
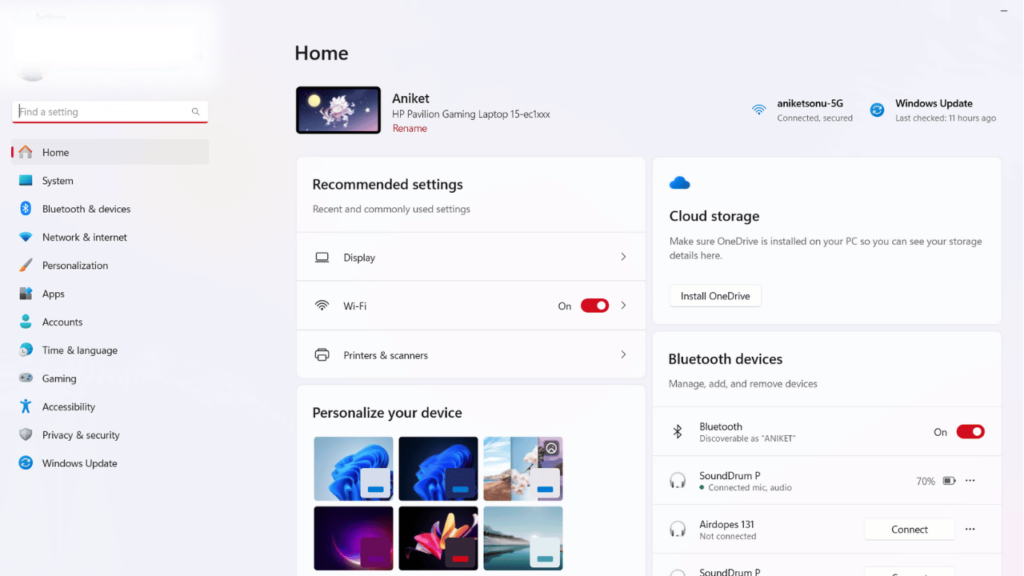
Step 2: Click System > About.
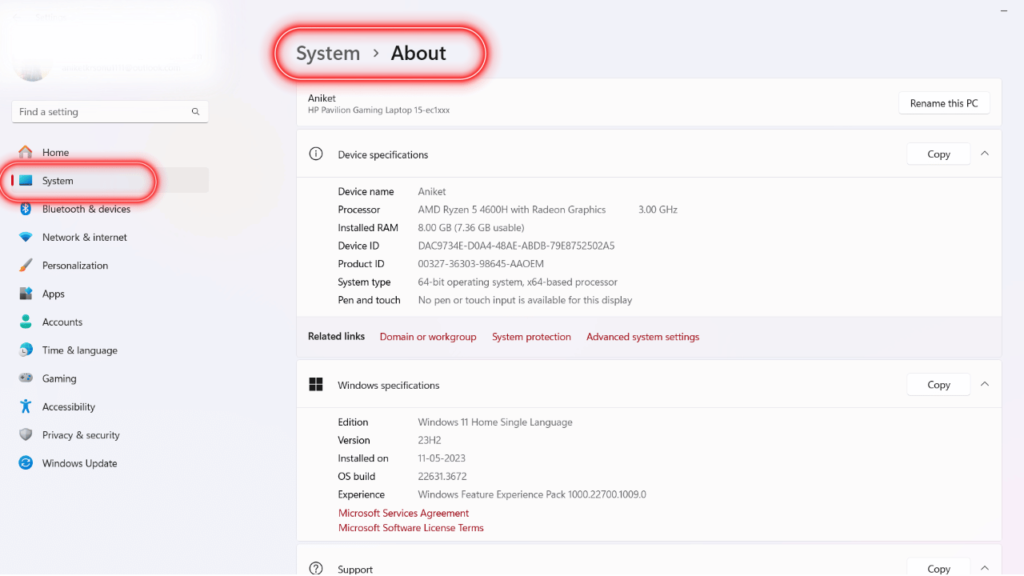
Step 3: Scroll down to the Related Links section and click Advanced system settings.
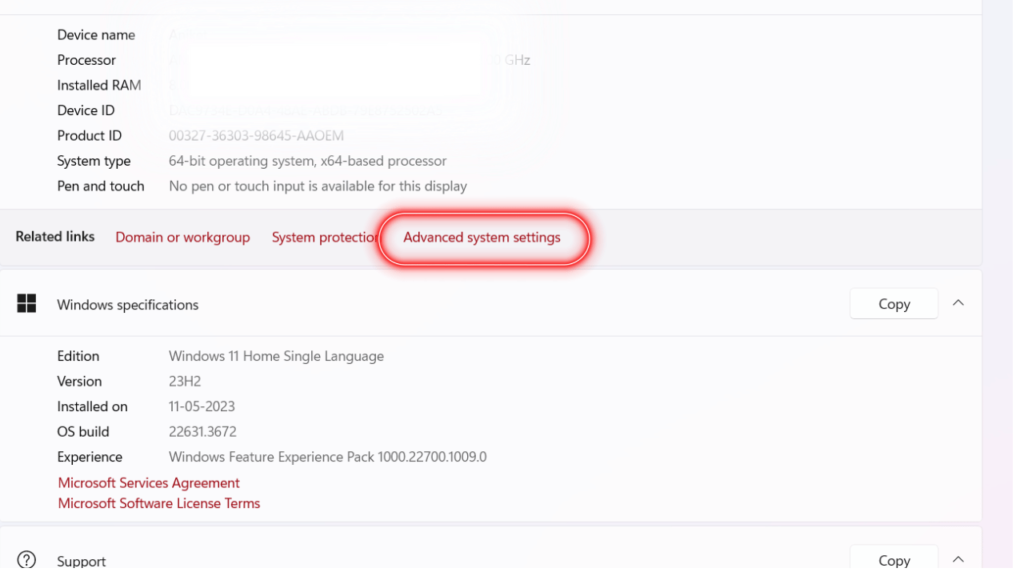
Step 4: In the Advanced tab of the System Properties window, click Settings in the Performance group.
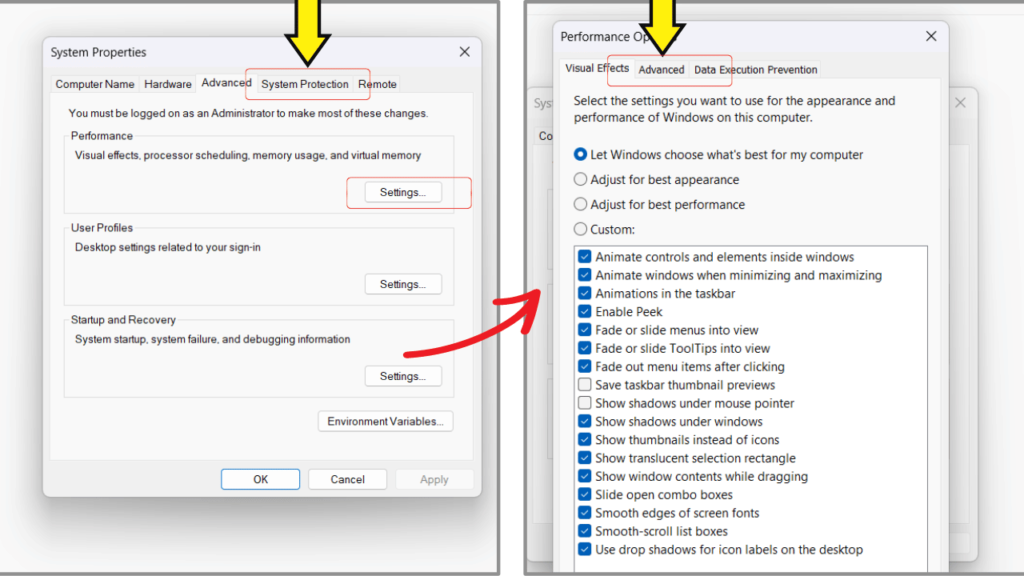
Step 5: In the Performance Options window, click Advanced > Change.
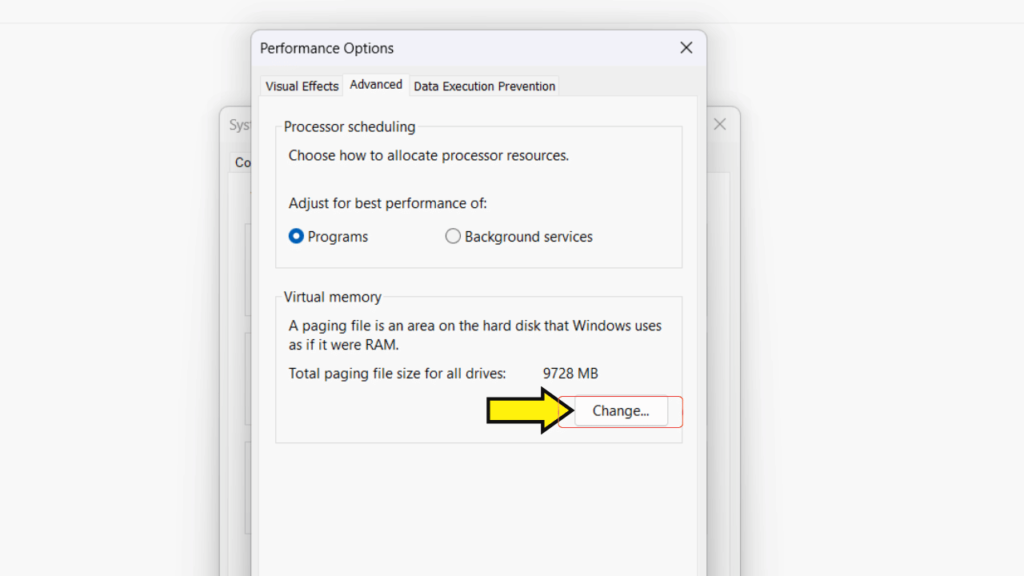
Step 6: Uncheck the box next to Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.
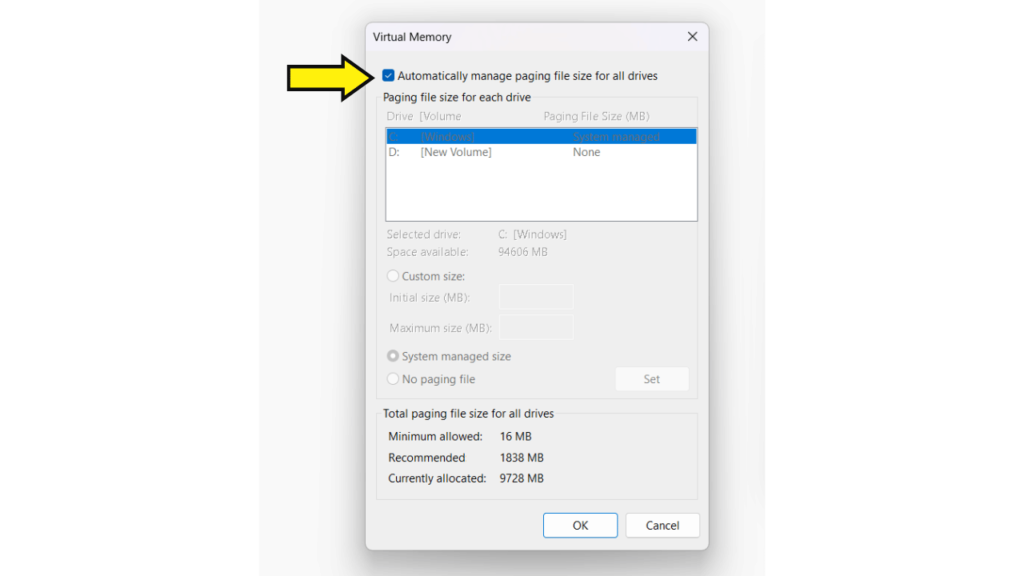
Step 7: Select the drive you want to manage.
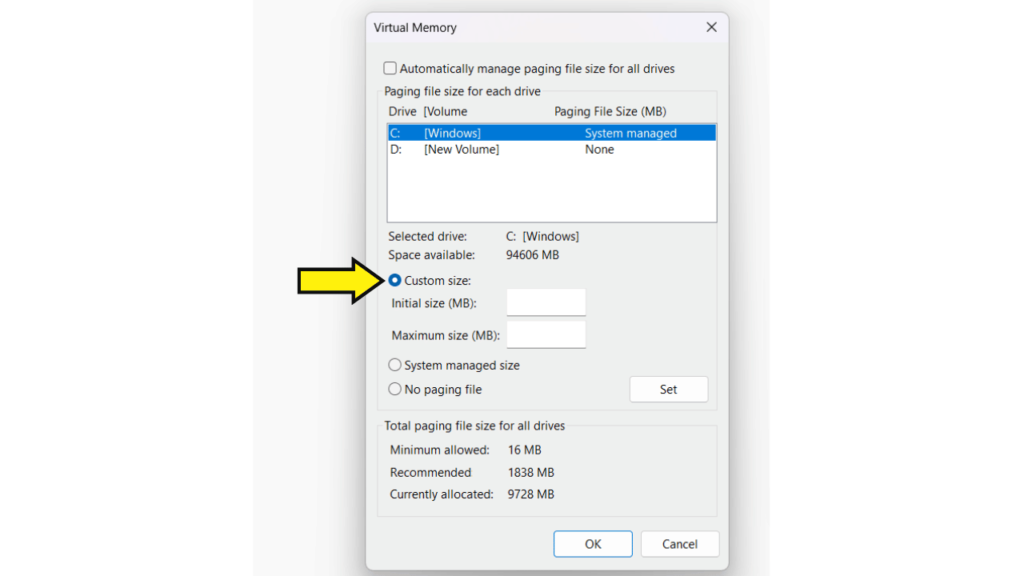
Step 8: Click Custom size and set the initial size (reserved space) and maximum size (limit it can grow to) for virtual memory (in MB).
| Initial Size Ram × 1.5 Maximum Size Ram × 3.0 | |
| For 4 GB RAM | Initial Size Ram = 4 × 1024 × 1.5 = 6144 Maximum Size Ram = 4 × 1024 × 3.0 = 12288 |
| For 8 GB RAM | Initial Size Ram = 8 × 1024 × 1.5 = 12288 Maximum Size Ram = 8 × 1024 × 3.0 = 24576 |
| For 16 GB RAM | Initial Size Ram = 16 × 1024 × 1.5 = 24576 Maximum Size Ram = 16 × 1024 × 3.0 = 49152 |
| For 32 GB RAM | Initial Size Ram = 32 × 1024 × 1.5 = 49152 Maximum Size Ram = 32 × 1024 × 3.0 = 98304 |
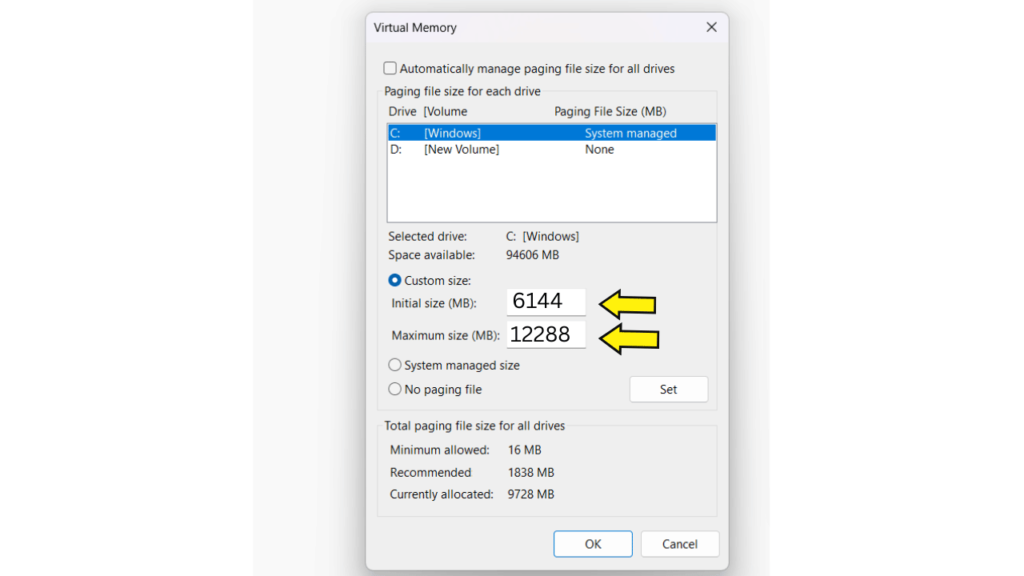
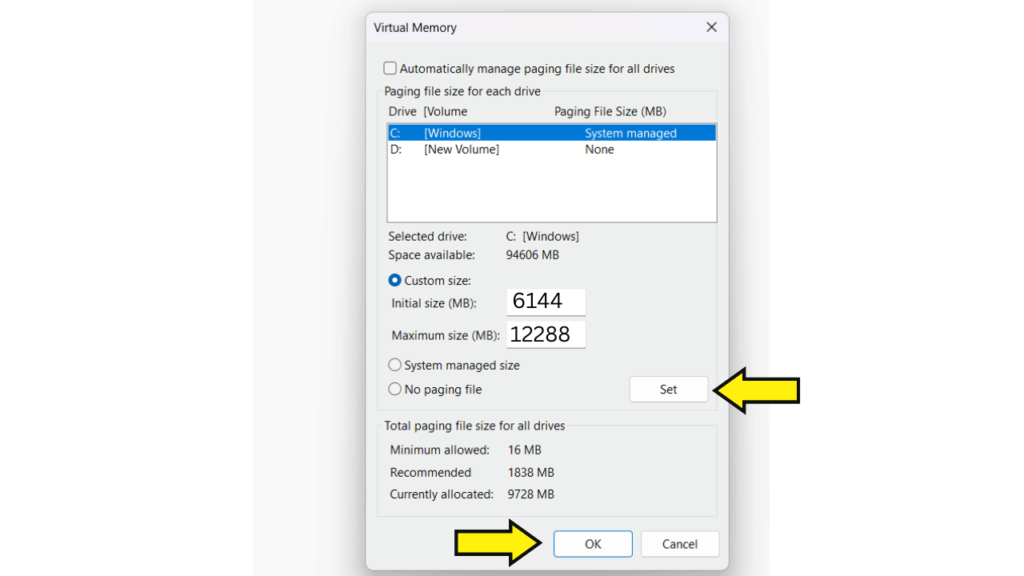
Step 9: Click Set > OK to confirm and restart the system.
How does virtual memory affect gaming?
Virtual memory doesn’t directly impact gaming performance or FPS. Let me explain:
- What Is Virtual Memory?: Virtual memory is like an extra space added to your system’s main memory (RAM) when needed. It’s an illusion that extends RAM by using part of your hard drive as additional memory.
- Compatibility: Virtual memory helps your system be compatible with some games. If your RAM is insufficient for a game, virtual memory can assist by providing extra space.
- Performance: However, virtual memory doesn’t boost performance or FPS. It’s not true RAM; it’s a pseudo-memory. When RAM is low, virtual memory transfers data between RAM and storage, making things smoother.
- VRAM Matters More: For gaming, focus on VRAM (Video RAM) instead. VRAM directly impacts graphics quality and load times. Modern games demand higher VRAM for detailed visuals and immersion.
In summary, virtual memory ensures compatibility but won’t significantly enhance gaming performance. Invest in sufficient RAM and VRAM for better gaming experiences.
Are there any risks in changing the paging file size?
Adjusting the paging file (virtual memory) size can impact system performance and stability. Here are some considerations:
- Insufficient Space: If you set a very small paging file size, your system may run out of virtual memory during resource-intensive tasks, leading to crashes or slowdowns.
- Fragmentation: Frequent resizing of the paging file can cause fragmentation, affecting read/write performance. It’s best to set a fixed size if possible.
- Storage Wear: Constant read/write operations on the paging file can wear out SSDs faster. HDDs are less affected, but still consider wear and tear.
- Page Faults: If the paging file is too small, you’ll experience more page faults (data retrieval from the disk), slowing down your system.
- RAM vs. Paging File: Increasing virtual memory doesn’t replace physical RAM. It’s a safety net when RAM is exhausted.
Recommendation:
- Set a reasonable initial and maximum size for the paging file (e.g., 1.5x to 3x your RAM size).
- Monitor system performance after changes to ensure stability.
Feel free to ask if you need further assistance.
How does increasing virtual memory affect performance?
Increasing virtual memory can impact performance in several ways:
- Performance Boost:
- When your RAM is fully utilized, the operating system uses the paging file (virtual memory) to store data that doesn’t fit in RAM.
- Increasing virtual memory provides more space for this overflow data, preventing slowdowns due to insufficient RAM.
- Slower access times:
- Virtual memory resides on your storage drive (HDD or SSD), which is slower than RAM.
- Accessing data from virtual memory takes more time, leading to performance degradation compared to RAM.
- Page Faults:
- Page faults occur when the OS needs to retrieve data from virtual memory.
- Frequent page faults can slow down your system significantly.
- Fragmentation:
- Resizing the paging file can cause fragmentation, affecting read/write performance.
- Set a fixed size to minimize fragmentation.
- Storage Wear (for SSDs):
- Constant read/write operations on the paging file can wear out SSDs faster.
- HDDs are less affected by this.
- Balancing Act:
- Adjust virtual memory based on your system’s needs and available resources.
- Monitor performance after changes to ensure stability.
Remember that virtual memory is a safety net when RAM is exhausted, but it’s not a substitute for physical RAM.
Can I disable the paging file altogether?
While it’s technically possible to disable the paging file (virtual memory) altogether, I recommend against it. Here’s why:
- System Stability:
- Windows relies on virtual memory for essential system processes and applications.
- Disabling it could lead to instability, crashes, or unexpected behavior.
- Low RAM Scenarios:
- If your RAM is fully utilized, the paging file acts as a safety net.
- Without it, your system might run out of memory, causing issues.
- Applications Expect It:
- Some applications assume the presence of a paging file.
- Disabling it might cause compatibility problems.
- Hibernation:
- If you use hibernation, the paging file is necessary.
- Disabling it would prevent hibernation.
Recommendation:
- Instead of disabling, consider adjusting the paging file size:
- Set a fixed size (initial and maximum) based on your system’s needs.
- Monitor performance to ensure stability.
Remember, virtual memory complements physical RAM—it’s not a replacement.
Also Read:-







Играйте в казино онлайн с удовольствием, выигрывайте большие суммы.
Проникнитесь атмосферой казино онлайн, играйте как профессионал.
Находите лучшие игровые площадки, следуйте советам экспертов.
Пополняйте свой счет с помощью казино онлайн, делая ставки на спортивные события.
Присоединяйтесь к сообществу азартных игроков, получайте удовольствие от игры.
Преуспейте в мире азартных игр, достигайте финансовой независимости.
Почувствуйте реальный азарт игры в казино онлайн, становясь настоящим профи.
Разнообразие игр ждет вас в онлайн казино, играйте на любом устройстве.
Преуспейте в азартных играх вместе с нами, зарабатывайте крупные суммы.
Превратите свой телефон в настоящее казино, погружаясь в мир азарта.
Разнообразные игры помогут вам насладиться моментом, удовлетворяя жажду азарта.
Станьте лидером в мире игр, завоевывая новые вершины.
Играйте в казино онлайн без ограничений, достижения ждут вас.
Улучшайте свои навыки игры в казино онлайн, практикуя различные подходы.
онлайн казино беларусь казино беларусь .
На сайте https://ricc-spb.com/sitemap/ узнайте всю необходимую информацию про гражданство Израиля. Кроме того, вы узнаете и о том, кто может рассчитывать на гражданство при заключении брака. Здесь представлен любопытный и интересный контент и на другую смежную тему. Он написан настоящими экспертами, которые отлично разбираются в таком вопросе. А новый контент публикуется на регулярной основе. Вы узнаете и о том, как отыскать еврейские корни по фамилии. Здесь находится полная, исчерпывающая информация, которая даст ответы на многочисленные вопросы.
Услуги дренажа по Озёрскому району Работаем без выходных.https://drenaj-mos.ru/
Обшивка бань и саун в г. Алматы и Алматинской области https://leshiy.kz/ – наша компания занимается внешней и внутренней обшивкой парных, саун и бань уже более 5 лет. Мы знаем, что каждая баня уникальна, поэтому мы подходим к каждому проекту индивидуально, учитывая комплектацию и технические характеристики помещения. Доверяя нам, каждый наш клиент может быть уверен в качестве и надежности нашей работы.
клинкерные ступени цена
исследование рынка льняных тканей в россии исследование рынка соевого соуса в россии
исследование рынка стеклянной посуды в россии исследование рынка бурильных труб в россии
исследование рынка крахмала в россии исследование рынка сои в россии
исследование рынка каустической соды в россии исследование рынка антибиотиков в россии
исследование рынка торфа в россии исследование рынка электроэнергии в россии
Автогалактика – это автоломбард, который оперативное получение денег предоставляет. Работаем честно и прозрачно, мы о своей репутации заботимся. Постоянно стремимся к развитию. Гарантируем вам индивидуальный подход. https://www.avtogalaktika.com – сайт, где имеется кредитный калькулятор, воспользуйтесь им. Также здесь можно оставить заявку. Для этого нужно ввести номер телефона и ваше имя в специальные поля. Мы свяжемся с вами в ближайшее время, чтобы обговорить наше дальнейшее взаимодействие. С нами безопасно и надежно!
исследование рынка фосфорной кислоты в россии исследование рынка пищевых субпродуктов в россии
Double рулетки что это? (Double от англ. удвоение). Это режим как в казино, в котором вам нужно выбрать цвет (в основном у всех рулеток это красное-черное-зеленое, но бывают и исключения например терористы-контр терористы) который выиграет. Красный и черный цвет это удвоение ставки – х2, зеленый цвет это когда ставка умножается на х14! Предположим я ставлю 1.000 монет на зеленое, и 5.000 монет на красное. Если выпадает черное то я проигрываю эти ставки.
В данном разделе https://dzen.ru/a/Z06KABuTmCJLDDgJ находится список рулеток CS:GO на красное-черное-зеленое с халявными промокодами на бесплатные монеты.
На сайте https://stream-series.net/ вы найдете огромное количество интересных, любопытных фильмов, сериалов, мультфильмов на самый взыскательный вкус. Также есть и аниме. Все это представлено в огромном количестве, в хорошем качестве, что позволит подобрать вариант для просмотра. Смотреть фильмы вы сможете в любое время и независимо от устройства, в том числе, на планшете, ПК. Насладитесь отличным звуком, огромным выбором фильмов самых разных жанров. Также есть раздел, в котором представлено лучшее кино за неделю. Регулярное обновление сериалов, кино.
исследование рынка детского питания в россии исследование рынка маргарина в россии
Временная регистрация в Санкт-Петербурге: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в СПБ?
Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов.
Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Временная регистрация в СПБ
Услуги монтажа канализаций по Мытищинскому району Работаем без выходных.https://drenaj-mos.ru/
На сайте https://chempionov.ru/ запишитесь в школу тенниса «Чемпион», где проходят увлекательные, интересные занятия по одноименному виду спорта. Предусмотрены 4 направления занятий: для взрослых, детей, предусмотрены индивидуальные либо групповые занятия. Используется международная техника обучения. Есть возможность воспользоваться арендой инвентаря, которая предоставляется абсолютно бесплатно. Все тренеры являются компетентными и проверенными, поэтому многому научат. Вы быстро освоите дисциплину.
Чтобы обходить блокировки, используйте доступ на mirror1win.ru. Этот инструмент позволяет непрерывный доступ.
купить метадон гашиш марихуану цена мефедрона в москве
снять шлюху индивидуалку порно вызвал шлюху а приехала сестра
https://rus-srubi.ru/vybor-fasadnoj-klinkernoj-plitki.html
Ваш проводник в мире права https://legallurist.ru актуальные статьи, комментарии юристов, новости законодательства и ответы на важные вопросы
Актуальные материалы по юриспруденции https://lawdelov.ru законы, практические рекомендации, разбор сложных ситуаций.
Ваш гид https://pravovoeob.ru в мире правовых норм: обязанности граждан, защита прав, полезные рекомендации и новости законодательства.
Ваш проводник в мире права https://legallurist.ru актуальные статьи, комментарии юристов, новости законодательства и ответы на важные вопросы
Ваш гид https://pravovoeob.ru в мире правовых норм: обязанности граждан, защита прав, полезные рекомендации и новости законодательства.
Актуальные материалы по юриспруденции https://lawdelov.ru законы, практические рекомендации, разбор сложных ситуаций.
Услуги дренажа по Красногорскому району Работаем без выходных.https://drenaj-mos.ru/
Сайт о налогах https://nalogido.ru изменения в законах, советы по декларированию и минимизации налоговых рисков.
Сайт о налогах https://nalogido.ru изменения в законах, советы по декларированию и минимизации налоговых рисков.
PicusBlog https://picusblog.com a blog with an American flavor. We cover news, celebrities, food, sports, nature, travel, animals, relationships and many other things that interest Americans (and not only) every day! PicusBlog – Your Daily Dose of Insights, Intrigue, and Inspiration!
Журнал для юристов https://zakonwin.ru практические советы, правовая аналитика, актуальная судебная практика и готовые инструменты.
Практический журнал https://uristvzakon.ru для юриста: аналитика, советы, готовые решения. Помощь в работе над делами любой сложности.
PicusBlog https://picusblog.com a blog with an American flavor. We cover news, celebrities, food, sports, nature, travel, animals, relationships and many other things that interest Americans (and not only) every day! PicusBlog – Your Daily Dose of Insights, Intrigue, and Inspiration!
Журнал для юристов https://zakonwin.ru практические советы, правовая аналитика, актуальная судебная практика и готовые инструменты.
Практический журнал https://uristvzakon.ru для юриста: аналитика, советы, готовые решения. Помощь в работе над делами любой сложности.
Если вы игрок в CS2 или ГО, то у вас наверняка неплохой инвентарь с множеством скинов, которые, будем честны, иногда попросту надоедают. И что же делать в такой ситуации? Продавать скины на Торговой площадке Steam – не вариант, там вас будут ждать заниженные цены и постоянные зависания, это уже не говоря о том, что гарантий на покупку вашего предмета попросту нет. ТУТ:https://dzen.ru/a/Z07p_ThRgyt0ppo9 вы можете вывести скины КС ГО и обменять их на новые или же получить деньги на карту в течение 15 минут.
клинкерная плитка купить
Профессиональные сантехнические услуги https://moskva-santehnicheskie-raboty.ru установка, ремонт и замена сантехники, устранение протечек, прочистка труб. Работаем быстро, качественно и с гарантией. Оперативный выезд и доступные цены. Ваш комфорт – наша забота!
Качественные услуги сантехника https://santehnik-na-dom-moscow.ru от мелкого ремонта до сложных систем. Замена труб, установка сантехники, устранение аварий. Работаем аккуратно, быстро и с гарантией. Звоните, и мы решим вашу проблему!
Права граждан РФ https://pravoup.ru доступные объяснения законодательства, практическая помощь и актуальные новости.
Консультации врачей онлайн https://onlinvrach.ru диагностика, анализы, контроль лечения. Все для вашего здоровья, не выходя из дома.
Профессиональные сантехнические услуги https://moskva-santehnicheskie-raboty.ru установка, ремонт и замена сантехники, устранение протечек, прочистка труб. Работаем быстро, качественно и с гарантией. Оперативный выезд и доступные цены. Ваш комфорт – наша забота!
Качественные услуги сантехника https://santehnik-na-dom-moscow.ru от мелкого ремонта до сложных систем. Замена труб, установка сантехники, устранение аварий. Работаем аккуратно, быстро и с гарантией. Звоните, и мы решим вашу проблему!
Права граждан РФ https://pravoup.ru доступные объяснения законодательства, практическая помощь и актуальные новости.
Консультации врачей онлайн https://onlinvrach.ru диагностика, анализы, контроль лечения. Все для вашего здоровья, не выходя из дома.
Временная регистрация в Санкт-Петербурге: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в СПБ?
Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов.
Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Временная регистрация в СПБ
Приобретение школьного аттестата с официальным упрощенным обучением в Москве
На сайте https://wing-chun-iwco.ru/ не упустите возможности записаться в популярную школу Вин Чун, которая находится в Москве. Она отличается официальным статусом, считается членом Федерации Вин Чун в нашей стране. В этой школе действительно эффективно и качественно обучают. А все потому, что преподаватели обладают всеми необходимыми знаниями, которые они передают своим ученикам. При этом Вин Чун против того, чтобы использовать силу в противовес другой силе. Разработана такая система, которая принципиально отличается от других искусств.
Услуги дренажа по Ленинскому району Работаем без выходных.https://drenaj-mos.ru/
продажа металлических бытовок бытовка железная купить
Все о ваших правах https://agkonsult.ru это портал, где вы найдете полную информацию о ваших гражданских, трудовых, семейных и других правах
Консультация юриста https://konsultantok.ru ваш помощник в решении юридических вопросов. Услуги профессиональных юристов, онлайн-консультации, полезные статьи.
Портал о ваших правах https://pravovoeobesp.ru это база знаний о законах, правах и обязанностях. Сайт создан для тех, кто хочет защищать свои интересы, получать ответы на юридические вопросы.
производство бытовок и блок контейнеров аренда бытовок санкт петербург
Все о ваших правах https://agkonsult.ru это портал, где вы найдете полную информацию о ваших гражданских, трудовых, семейных и других правах
Консультация юриста https://konsultantok.ru ваш помощник в решении юридических вопросов. Услуги профессиональных юристов, онлайн-консультации, полезные статьи.
Портал о ваших правах https://pravovoeobesp.ru это база знаний о законах, правах и обязанностях. Сайт создан для тех, кто хочет защищать свои интересы, получать ответы на юридические вопросы.
kraken
kra19
Юридическая помощь автолюбителям https://avtopravodo.ru ваш надежный источник информации о правах водителей. Разбор ДТП, штрафы, страховые споры, возврат прав – все, что нужно для защиты ваших интересов.
Статьи для вас и вашего бизнеса https://businessfaq.ru подборка актуальных материалов для предпринимателей. Советы по управлению, развитию, финансам и маркетингу, чтобы ваш бизнес процветал.
Бизнес статьи https://consultantdo.ru платформа для предпринимателей. Полезные материалы, аналитика и советы экспертов для успешного управления бизнесом, развития и повышения прибыли.
Права и обязанности граждан https://juristywin.ru это ресурс для тех, кто хочет знать свои права, соблюдать законы и уверенно решать правовые вопросы.
Юридическая помощь автолюбителям https://avtopravodo.ru ваш надежный источник информации о правах водителей. Разбор ДТП, штрафы, страховые споры, возврат прав – все, что нужно для защиты ваших интересов.
Бизнес статьи https://consultantdo.ru платформа для предпринимателей. Полезные материалы, аналитика и советы экспертов для успешного управления бизнесом, развития и повышения прибыли.
Статьи для вас и вашего бизнеса https://businessfaq.ru подборка актуальных материалов для предпринимателей. Советы по управлению, развитию, финансам и маркетингу, чтобы ваш бизнес процветал.
Права и обязанности граждан https://juristywin.ru это ресурс для тех, кто хочет знать свои права, соблюдать законы и уверенно решать правовые вопросы.
Ищите грузоперевозки в Минске? Зайдите на сайт https://gruzoff.by/ и вы сможете заказать машину и грузчиков, вывоз мусора, которые приедут за 30 минут. Город и межгород. А наши цены понравятся каждому. Узнайте тарифы на сайте. Нас ищут по запросам: грузоперевозки минск, грузоперевозки, перевозка груза, грузовое такси, мотоэвакуатор минск, мотоэвакуация, вывоз мусора минск, утилизация мусора.
Услуги монтажа канализаций по Подольскому району Работаем без выходных.https://drenaj-mos.ru/
Зачем откладывать на потом? Печи утилизаторы отходов уже ждут вас! Удобные, простые и безопасные в использовании, эти устройства помогают утилизировать мусор без вреда для окружающей среды. Хотите узнать больше? Загляните на сайт и найдите оборудование, которое решит ваши проблемы.
Временная регистрация в СПб: Быстро и Легально!
Ищете, где оформить временную регистрацию в Санкт-Петербурге?
Мы гарантируем быстрое и легальное оформление без очередей и лишних документов.
Ваше спокойствие – наша забота!
Минимум усилий • Максимум удобства • Полная легальность
Свяжитесь с нами прямо сейчас!
Временная регистрация
Устали искать решение для мусора? Установка для уничтожения отходов станет вашим помощником! Это оборудование эффективно справляется с утилизацией любых материалов. Идеальный выбор для предприятий, которые заботятся об экологии и порядке.
Не знаете, где приобрести по недорогой стоимости в Екатеринбурге мебель? Интернет-магазин «Ок-мебель» рад предложить вам прекрасную возможность обновить интерьер, даже если бюджет ограничен. Предоставляем разные варианты оплаты. Мебель высоким стандартам качества отвечает. Мы доставим ее точно в срок. https://ok-mebel.com – сайт, где вы сможете найти все, что вам нужно. Если у вас возникли какие-либо вопросы, можете обратиться к нашим высококвалифицированным менеджерам. Они с радостью предоставят необходимую информацию и окажут помощь в оформлении заказа.
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Услуги дренажа по Рузскому району Работаем без выходных.https://drenaj-mos.ru/
На сайте https://aleont.by/zenitnie-fonari/zenitnye-fonari-iz-polikarbonata/ уточните телефон для того, чтобы заказать зенитные фонари на самых выгодных условиях и по привлекательной стоимости. Они необходимы для того, чтобы в помещении сформировалось естественное освещение. Конструкции особенно незаменимы в тех случаях, если на фасаде здания не получится произвести монтаж окон. Конструкции, которые можно приобрести в этой компании, очень прочные, надежные, имеют долгий срок службы.
Maximitzeu els vostres rendiments en invertir . Aquesta guia us donara consells sobre com invertir a Austria i us ajudara a prendre decisions informades.
Услуги монтажа ливневок по Москве и МО Работаем без выходных.https://drenaj-mos.ru/
Ищите где купить обои в Смоленске? Зайдите на сайт компании Центр обоев Премьера https://smolensk.premiera-oboi.ru/ и вы найдете самый большой выбор обоев производства различных стран и брендов. Удобная сортировка – выбирайте материал обоев, цвет, для какой комнаты, какие будут узоры или стиль, а также воспользуйтесь 3D примерочной. Посмотрите каталог и наши акции – а также воспользуйтесь легким подбором обоев по параметрам. Вы можете забронировать товар и забрать его самостоятельно в магазине.
Как приобрести диплом о среднем образовании в Москве и других городах
На сайте http://oknaksa.ru вызовите замерщика для того, чтобы воспользоваться услугой, связанной с остеклением балконов, патио. На все материалы, конструкции предоставляются гарантии до 20 лет, а на установку до 60 месяцев. Каждый клиент получает возможность абсолютно бесплатно воспользоваться услугами замерщика. Он приедет в самое удобное для вас время. Все монтажные работы выполняются непосредственно в день замеров. Вы сможете воспользоваться огромным количеством готовых проектов и выбрать подходящее для себя решение.
светодиодные экраны москва светодиодные led экраны цена
Портал права и обязанности https://legallup.ru граждан помогает разбираться в законах, правах и обязанностях. Полезные статьи и инструкции для защиты своих интересов.
Моё право https://moepravodo.ru ваш гид по законодательству. Простые объяснения, полезные рекомендации и образцы документов для реализации и защиты ваших прав.
Права и обязанности граждан https://llawdo.ru источник знаний о ваших правах и обязанностях. Простая навигация и практическая информация для решения юридических вопросов.
цифровой светодиодный экран светодиодные led экраны цена
Портал права и обязанности https://legallup.ru граждан помогает разбираться в законах, правах и обязанностях. Полезные статьи и инструкции для защиты своих интересов.
Моё право https://moepravodo.ru ваш гид по законодательству. Простые объяснения, полезные рекомендации и образцы документов для реализации и защиты ваших прав.
Права и обязанности граждан https://llawdo.ru источник знаний о ваших правах и обязанностях. Простая навигация и практическая информация для решения юридических вопросов.
светодиодные led экраны цена светодиодные экраны для помещения
На сайте https://lookshine.ru/ вы сможете заказать качественную, красивую одежду, аксессуары, а также обувь. Все это от легендарных, лучших брендов, которые следуют моде и создают настоящие произведения искусства, достойные вашего внимания. Все изделия стильные, аристократичные, отличаются продуманным дизайном. А самое важное, что они выполнены из инновационных материалов, поэтому одежда, обувь точно прослужат долго, не утратив внешнего вида. Доставка выбранной продукции осуществляется в течение часа.
https://www.cyberpinoy.net/read-blog/18288
светодиодный экран стоимость https://svetodiodnyy-ekran.ru
Maximitzeu els vostres rendiments en invertir pisos de Viena . Aquesta guia us donara consells sobre com invertir a Austria i us ajudara a prendre decisions informades.
светодиодный экран hd купить светодиодные экраны цена
Правовой ресурс https://pravoto.ru для тех, кто хочет знать свои права, защищать их и понимать законы. Актуальные статьи, инструкции и практическая информация для каждого.