The BitLocker recovery key is your lifeline when you encounter access issues with encrypted drives. If you find yourself in a situation where you need to recover this key, fret not—we’ve got you covered. In this informative post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of locating the BitLocker recovery key, ensuring that you’re well-equipped to handle any data recovery scenario. Whether you’re utilizing built-in Windows features or exploring third-party solutions, our expert tips will streamline the process and empower you to regain control of your encrypted data.
Table of Contents
What is BitLocker?
BitLocker is a Windows security feature that provides encryption for entire volumes, addressing the threats of data theft or exposure from lost, stolen, or inappropriately decommissioned devices. Here are some key points about BitLocker:
- Purpose: BitLocker encrypts data on your hard drive or other storage volumes to prevent unauthorized access. It ensures that even if someone physically steals your device or hard drive, they won’t be able to access the data without the decryption key.
- How It Works:
- Volume Encryption: BitLocker encrypts entire volumes (such as the operating system drive) rather than individual files or folders.
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM): For maximum protection, BitLocker works best when used with a TPM. A TPM is a hardware component installed on Windows devices that helps verify system integrity while the system is offline.
- Startup Authentication: BitLocker can require a PIN or a startup key stored on a removable drive during system startup. This provides multifactor authentication and ensures that the device can’t start without the correct credentials.
- No TPM Option: If your device doesn’t have a TPM, you can still use BitLocker, but it’s less secure. In this case, you’ll need to use a startup key or a password for encryption.
- System Requirements:
- TPM: For TPM-based protection, your device must have TPM 1.2 or later versions.
- TCG-Compliant BIOS/UEFI: If your device has a TPM, the BIOS or UEFI firmware must be TCG-compliant and support static root of trust measurement.
USB Mass Storage Support: The system BIOS or UEFI firmware (for both TPM and non-TPM devices) must support reading files from a USB drive during preboot.
In summary, BitLocker is a powerful tool to protect your data, especially when combined with a TPM. It ensures that your information remains confidential even if your device falls into the wrong hands. If you’re using Windows, I recommend exploring BitLocker to enhance your data security.
How to Enable and Disable Bitlocker.
- Enabling BitLocker:-
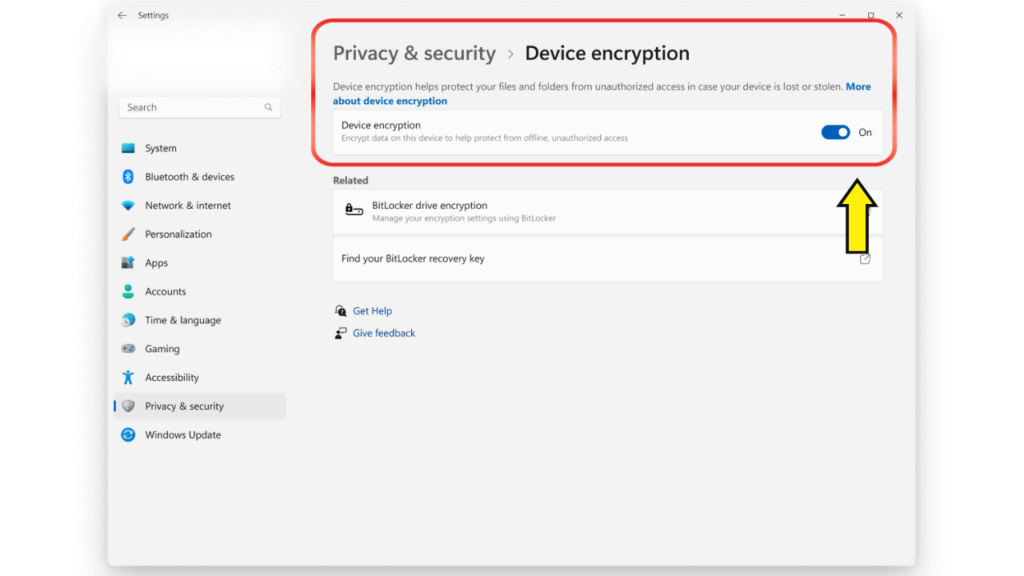
- Get the settings open.
- Select the option for Privacy and Security.
- Select the device encryption option.
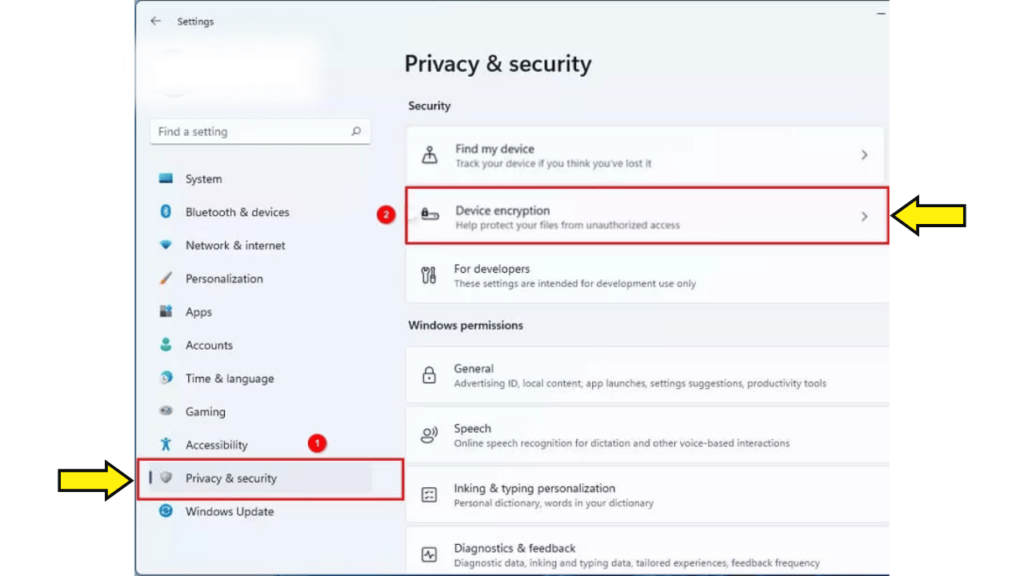
- Turn on or enable Bitlocker or device encryption.
2. Disabling BitLocker:-
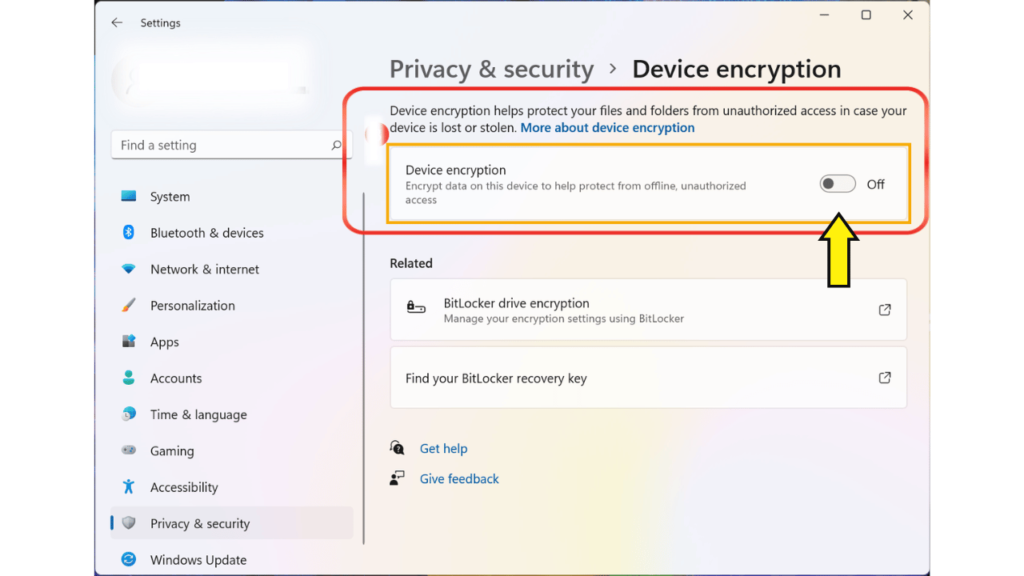
- Get the settings open.
- Select the Privacy and Security menu item.
- Select the device encryption option.

- Turn off or disable Bitlocker or device encryption.
How to find the BitLocker recovery key.
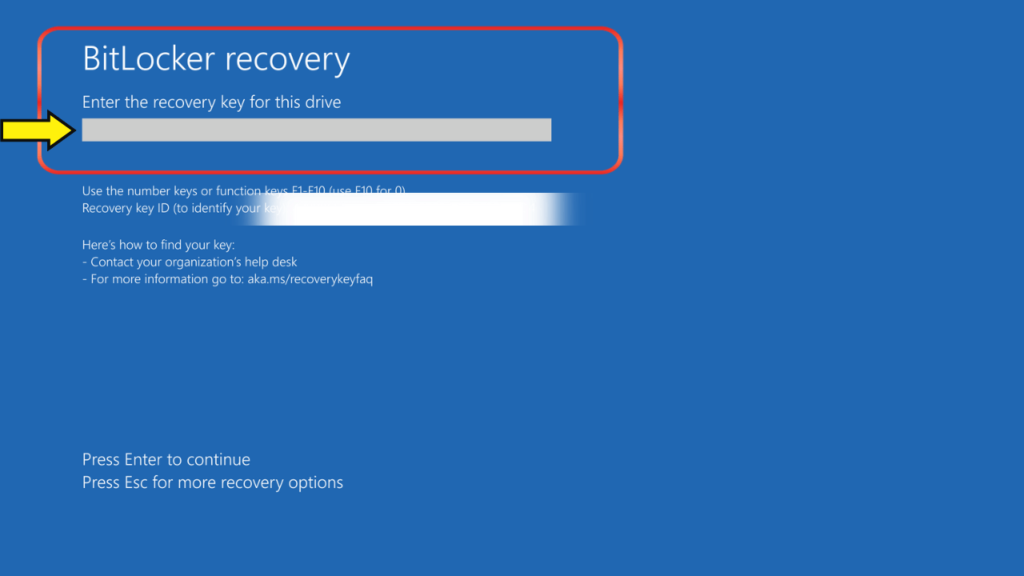
If you need to find your BitLocker recovery key, here are some ways to locate it:-
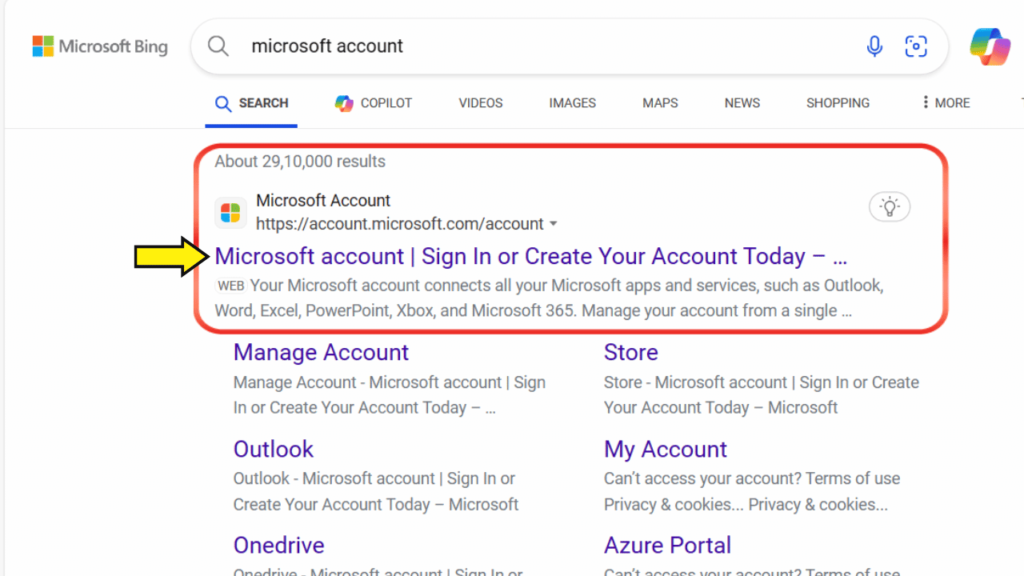
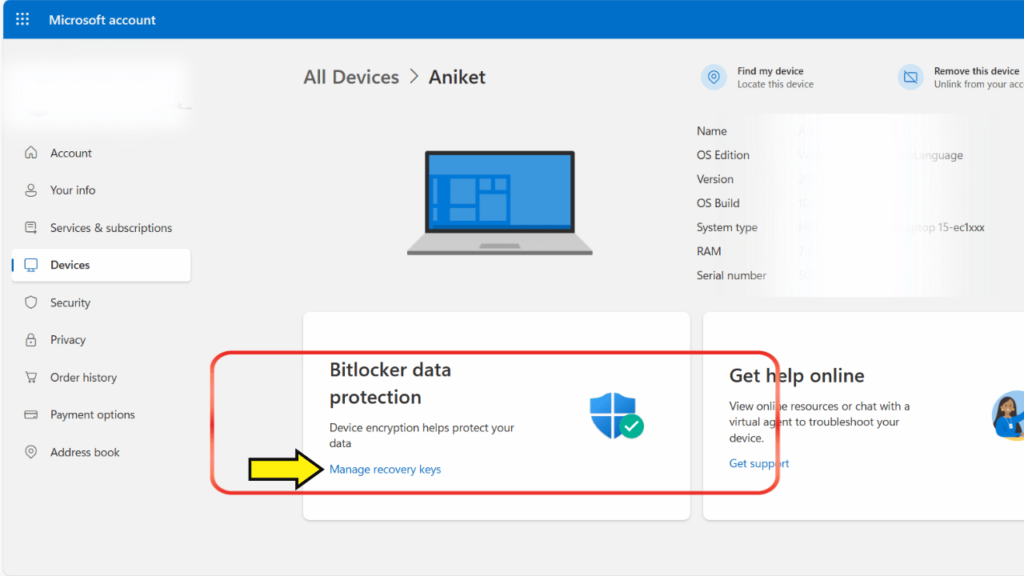
- Open a web browser on another device search Microsoft Account and open first link.
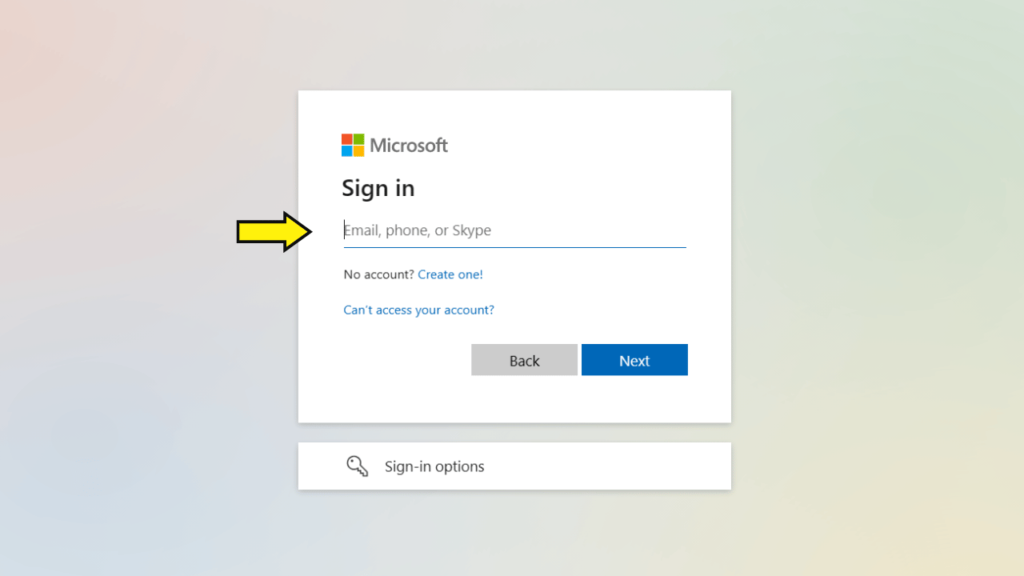
- Sign in with your Microsoft account credentials.
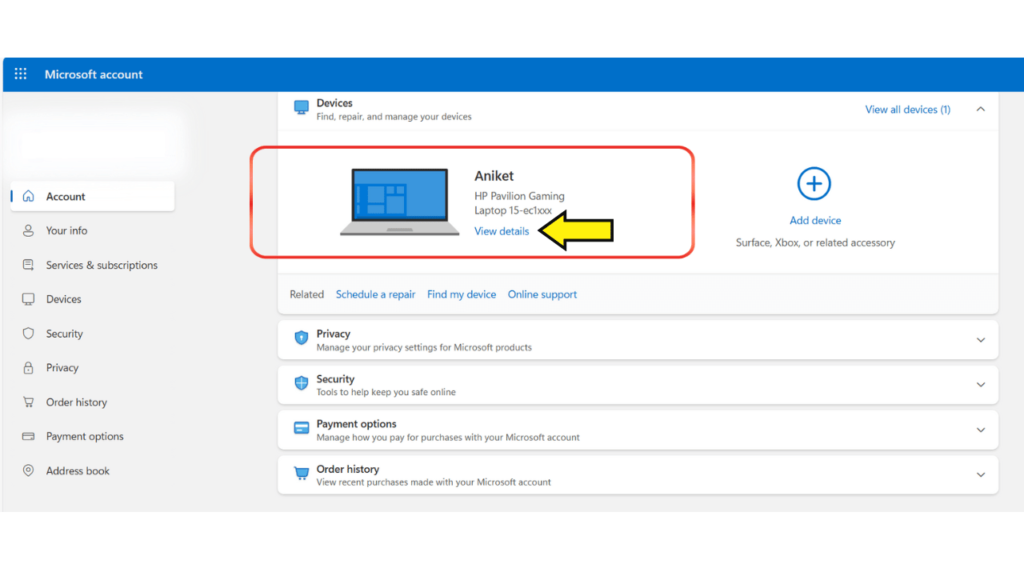
- Select Device and then Click View Details.
- Choose “Manage Recovery Key.”
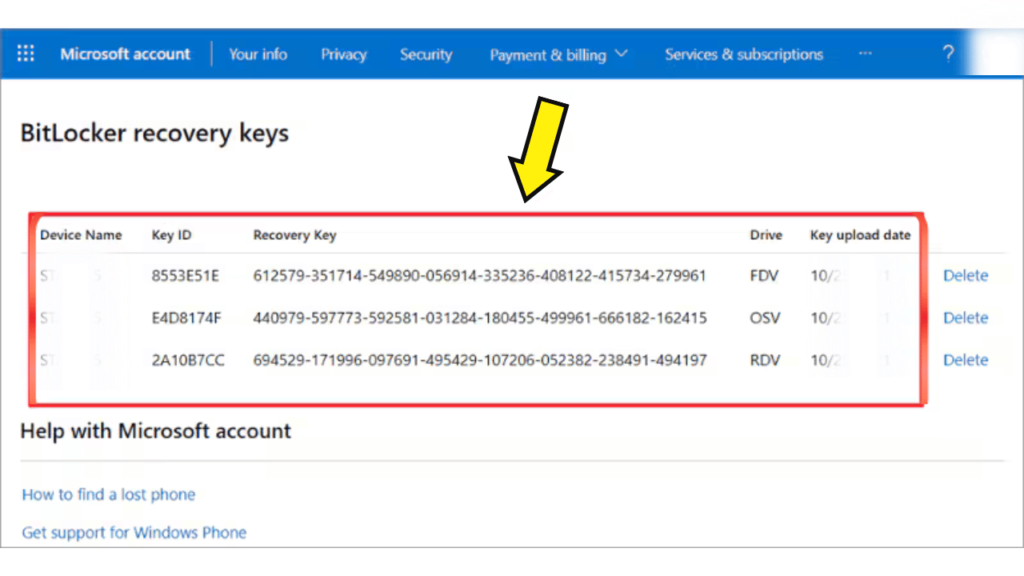
- The BitLocker recovery key should be displayed.
Difference between BitLocker and device encryption
Let’s explore the difference between Device Encryption and BitLocker:
- Device Encryption:
- Purpose: Device encryption is a security feature available on every Windows edition (provided your hardware supports it). It automatically encrypts your system and secondary drives, ensuring that unauthorized individuals cannot access your data if your laptop or device is lost or stolen.
- Configuration: Device encryption has no configurable options. It relies solely on the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) chip for security.
- User Requirements: To use device encryption, you need an active TPM and must be signed in to a Microsoft account. The recovery key is uploaded to your OneDrive account.
- Suitability: Device encryption is well-suited for consumer end users.
- BitLocker:
- Availability: BitLocker is available in Windows 11/10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education editions. It is not included in the Windows 11/10 Home edition.
- Purpose: BitLocker is a comprehensive volume encryption technology. It allows you to selectively encrypt single drives or all drives on your PC.
- Management Tools: BitLocker provides a set of management tools, making it suitable for business use.
- Configuration: You can configure BitLocker via Group Policy (GPO) and back up the recovery key to a location of your choice.
- Hardware Requirements: BitLocker requires a TPM (either TPM 1.2 or TPM 2.0) and UEFI Secure Boot enabled.
In summary, device encryption automatically encrypts your entire system, while BitLocker offers more flexibility and management controls for selective drive encryption. Choose the one that best fits your needs and hardware configuration.
Also Read:-